Biomedical
Novel Ligands for Serotonin Receptor 2B (5-HT2B)
There are multiple diseases affecting the central nervous system (CNS) including Alzheimer’s & Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, drug abuse, and addiction. However, there is currently a void in the tools available for the treatment and study of such CNS related disorders. This void can lead to inaccurate diagnosis and delayed treatment, ultimately increasing patients’ mortality and associated morbidity. The 5-HT2B receptor is emerging as a valuable pharmacological target to treat such diseases. Available compounds do not provide the needed selectivity or high inhibitory actions to address current needs. Thus, new developments are needed to further the application of 5-HT2B receptor antagonist for the treatment of these neurological diseases.
The technology
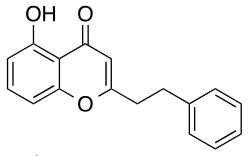
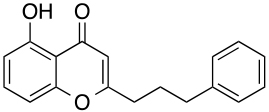
This technology addresses the unmet need of selective 5-HT2B ligands used to treat and study a number of CNS related disorders. This ligand can be readily synthesized and easily manipulated and has shown high selectivity towards the 5- HT2B receptor with very low affinity to other receptors in the 5-HT2 family. Selectivity for the 5-HT2B is remarkable as very few ligands have demonstrated such selectivity. The development of this novel ligand also has possible therapeutic applications that allow for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases in the CNS as well as irritable bowel syndrome, migraine headaches, and pulmonary hypertension.
| Compound | % Inhibition (Ki) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2A | 5-HT2B | 5-HT2C | |
|
1st Generation |
14.2 | 62.6 (2.5 μM) | 4.8 |
|
2nd Generation |
5.4 | 70.4 (240 nM) | 7.9 |
Table 1. In vitro studies have demonstrated the high selectivity and inhibitory response of the ligand.